Snaps security guidelines
This page outlines essential principles for builders to develop secure and reliable Snaps. Use these guidelines when creating your Snap to ensure it is safe for users.
Manage permissions
The following are guidelines for managing permissions in the Snap manifest file.
-
Minimum permissions - Follow the principle of least authority by only adding the minimum permissions needed by your Snap in the manifest file. Before publishing your Snap, check the permissions again and remove any unused permissions. You can validate your permissions using the Snaps Simulator Manifest Validator.
-
Minimum RPC access - When adding the
endowment:rpcpermission for Snaps or dapps, ask yourself if both are necessary. For example, if permission is granted to communicate with Snaps, it means other Snaps can call your Snap's sensitive RPC methods. -
Minimum network access - Only add the
endowment:network-accesspermission if it's absolutely necessary, such as when needing to communicate with a remote API that is part of your Snap's functionality. This to mitigate users' concern about sharing wallet usage to remote servers. If your Snap needs this permission, inform the user before communicating with remote servers and include a privacy policy in your Snap that explains how data is shared.
Handle transactions securely
The following are guidelines for handling and signing transactions:
-
Transaction details - When handling transactions, provide a prompt displaying all transaction details, including the receiver address, chain ID, network, and amount. Display the originating site's domain name and the target blockchain. Ensure the user verifies the receiver address to avoid sending funds to an incorrect destination.
-
Transparent signing - Display the message to be signed by the user in the Snap confirmation flow. Do not rely on the requesting site to display this message, as it might choose not to, leading to the Snap signing the message silently.
-
Consentful confirmations - Before signing a transaction, display a user confirmation prompt with all the transaction details as previously mentioned.
Notify users
The following are guidelines for user notifications, dialogs, and authorizations:
-
Transparent and consentful actions - Before performing any of the following actions, display a confirmation dialog that contains detailed information about the action and asks the user to reject or accept it:
- Modifying or reading state. (In general, notify the user about any state changes.)
- Switching networks or accounts.
- Deriving or generating key pairs, accounts, or smart contracts.
- Signing transactions. (If your Snap is designed to allow automatic transactions, prompt the user before enabling this and make sure they know how it works. Also provide a way to disable it.)
-
Protect user keys - Do not allow your Snap to return all user wallet addresses to the site, even public keys. Users should choose and authorize the addresses to expose.
-
Limit access to sensitive methods - When building a Snap with sensitive RPC methods, use a companion dapp as an "admin interface" to interact with your Snap's sensitive methods. There are two ways to do this:
-
Restrict the
endowment:rpcpermission to specific URLs using theallowedOriginscaveat. -
Filter specific methods to specific URLs using the built-in URL library:
const referrer = new URL(origin);
if(referrer.protocol === "https:" &&
(referrer.host.endsWith(".metamask.io") || referrer.host === "metamask.io")) {
console.log("URL is valid");
}
else {
console.log("URL is NOT valid");
}In this example, the RPC method can be restricted when the origin matches
https://metamask.ioor any subdomain. This check can be used on any RPC method that should not be callable by all sites.noteAvoid using regular expressions or string matching to filter URLs. The URL library provides a much more reliable interface for matching URLs.
-
Secure sensitive information
The following are guidelines for handling sensitive or personally identifiable information such as user IPs, emails, passwords, and private keys:
-
Logging - Remove all logs to the JavaScript console that contain sensitive information. Disable all logging before publishing your Snap.
-
Errors - Review parts of your code where errors and exceptions can be raised. In some cases, error stacks can be written to the console with sensitive information. This information can be captured in data logs, or a malicious actor can phish the user into copying and sending the error.
-
Private keys - Avoid retrieving the user's private key from the Snap unless absolutely necessary, such as to sign a transaction. If you only need the user's public key, use
snap_getBip32PublicKeyinstead of deriving it from the private key. Never return the private key in an RPC method to a dapp or another Snap. To give users a way to view their private key, display it in a dialog. -
Limit exposure - Avoid accidentally returning sensitive information from a method. For example, you might have a method that intends to return sensitive information only in specific cases, but due to a typo or bad logic, it returns the information incorrectly, leaking data. Even if you have a legitimate reason for allowing a user to export sensitive information, you should prevent that information from being revealed carelessly (similar to how MetaMask makes it difficult to reveal a Secret Recovery Phrase and for an observer looking over a user's shoulder to see it).
When in doubt, choose friction over convenience for sensitive information.
Validate parameters
The following are guidelines for validating RPC parameters and handling values:
-
Validate user inputs - Validate and sanitize user inputs coming into the Snap-exposed RPC methods. Never assume a parameter is safe to use. If unvalidated user inputs are used inside the logic of your Snap methods, a dapp or a user can exploit that logic in an unsafe way.
-
Get values from MetaMask - Get values such as chain ID or address from MetaMask instead of the dapp. A dapp can accidentally or maliciously display incorrect values, tricking users into performing certain actions (for example, signing a transaction for a network to which they didn't intend to broadcast the transaction). If a dapp provides values that do not match the values from MetaMask, warn the user in your confirmation flow.
-
Use
copyablefor safe disclosures - When displaying arbitrary content in a Snap dialog, such as for signing a message, use thecopyableuser interface component instead oftext. When using dialogs, the input may contain special characters that render as Markdown and can mislead the user. For example: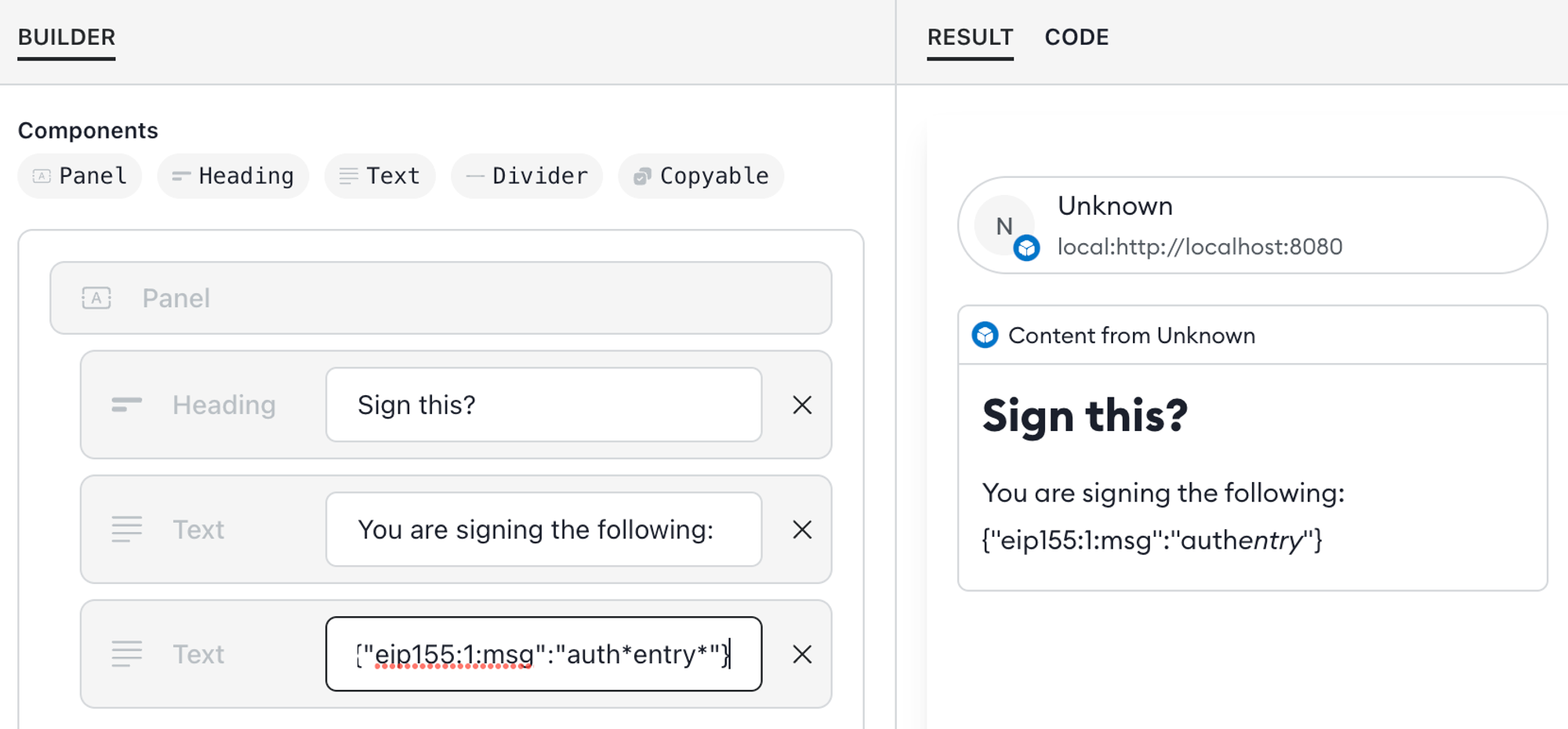
The special characters
*and_render Markdown formatting, so what the user sees does not match the content. To avoid this, usecopyableinstead: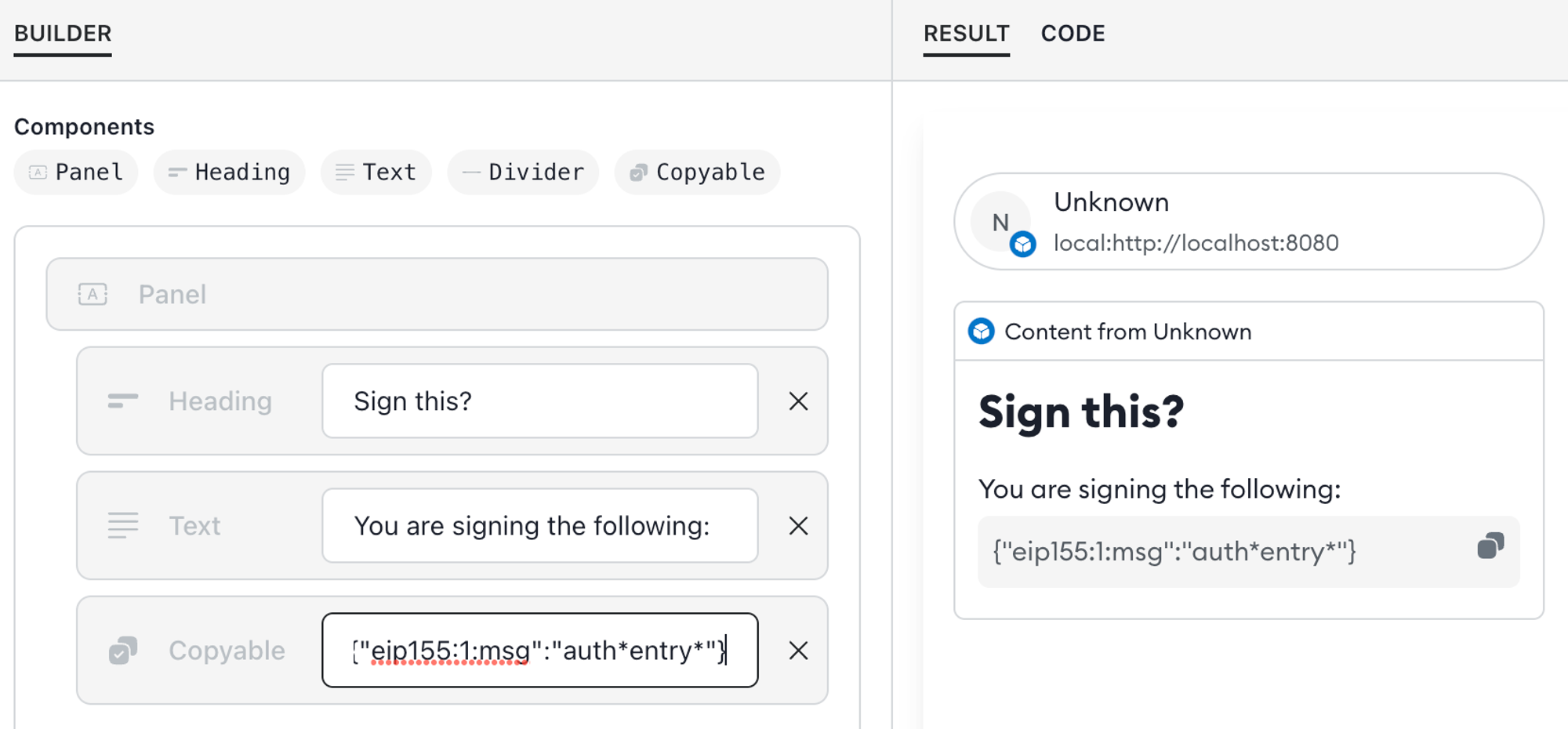
copyabledoes not render Markdown and has the added benefit that the user can select to copy the content. Also, the formatting provides a visual delineator to separate arbitrary input or fields from user interface text. -
Check transaction data size - Check the size of the ABI-encoded transaction data's function arguments. The ABI specification requires all arguments, regardless of their type, to be 32 bytes. If an argument is not 32 bytes, the calling contract's behavior might depend on the contract compiler version. For example, Solidity 0.5.0 treats these non-aligned arguments as invalid and reverts the function call. Older Solidity versions automatically append zeros at the end of the transaction data to ensure all arguments are 32 bytes. An attacker can exploit this feature to bypass security checks implemented in the corresponding contract function that reads those function arguments.
Avoid using deprecated methods
Avoid using the following deprecated methods:
-
wallet_enable, which is deprecated in favor ofwallet_requestSnaps. -
snap_confirm, which is deprecated in favor ofsnap_dialog. -
endowment:long-running, which is deprecated for MetaMask stable but still allowed in MetaMask Flask.
Coding best practices
The following are coding security tips and warnings:
-
SES compatibility - Use packages or libraries compatible with SES (hardened JavaScript). If you don't, you might encounter errors that require patching a specific dependency to fix.
-
Timers and side-channel attacks - Certain JavaScript features such as timers (for example,
Date.now) can expose critical system information, making a user vulnerable to side-channel attacks. In the Snaps execution environment, the precision of these timers has been reduced to prevent this. -
Unsafe cryptographic libraries - Avoid using unsafe cryptographic libraries. Do not use
Math.random, which is not sufficiently random for generating cryptographic hashes and can expose a user to reverse engineering or brute-forcing keys in the future. Do not use insufficient hashing algorithms such asmd5orsha2. Do not roll your own cryptography or use custom or unproven cryptography methods or libraries.We recommend using
snap_getEntropyfor entropy, the built-in Web Crypto API or Noble cryptography libraries, and safe hashing algorithms such assha256. Choose audited, widely used libraries over obscure, untested implementations.
Manage dependencies
The following are guidelines for securing your supply chain:
-
Pin npm package dependencies - Pin all npm package dependencies in the Snap's dependency tree to exact versions. If you don't, a supply chain attacker can trick you into including a malicious version of a package instead of the original, legitimate one. You can quickly check the status of your dependencies by running
npm auditin your Snap directory. -
Secure your stack - Your Snap companion dapp and any remote servers are part of your security model. We recommend using LavaMoat to secure relevant parts of your stack and following security best practices for your dapp or server.
Publish and serve your Snap
The following are guidelines for making your Snap available to users safely:
-
Snap updates - When serving a Snap from a dapp, make sure users are getting the latest version of your Snap. Do not allow any actions on the dapp before reconnecting it to MetaMask and loading a new or updated version of the Snap. This prevents users from using outdated versions of the Snap that may have potential bugs and security issues.
-
Snap publication - Ensure correct publication of the Snap. Only publish the
packages/snapfolder, and not the entire GitHub repository for a project. -
Other wallet extensions - Be aware that if the user has other wallet browser extensions installed, a call to the MetaMask provider
window.ethereumcan be overridden. Connect to Snaps using EIP-6963 to reliably access the MetaMask provider.
Conclusion
In general, when developing Snaps, put yourself in the user's shoes and consider how they use MetaMask. Always prioritize their privacy and the security of their assets.
If you have any questions or a security best practice not listed here, post it in the Snaps GitHub discussions.